Manual Machining vs. CNC Machining: What’s the Difference?
When it comes to creating precise parts and components, the manufacturing industry relies on two primary methods of machining: manual and CNC. Each has unique characteristics and advantages, and understanding these is crucial for manufacturers, engineers, and hobbyists alike.
So, what’s the difference between manual machining and CNC machining? Let’s explore the nature of each and consider the best ways to use them. With this knowledge, you’ll be empowered to select the most suitable method for producing high-quality products efficiently and cost-effectively.
Manual Machining
Manual machining is a traditional approach that involves the use of manually operated machines, such as lathes, milling machines, and drill presses. In this process, skilled machinists control and adjust the machinery by hand, relying on their expertise and experience to complete the work. Manual machining allows for a high degree of flexibility and adaptability, making it suitable for custom or smaller-scale projects where precision is paramount.
Although it requires more time and attention, manual machining can be more cost-effective for particular jobs, especially when producing low-volume or prototype parts. Additionally, it provides invaluable training opportunities for machinists to develop a deeper understanding of machining principles and techniques.
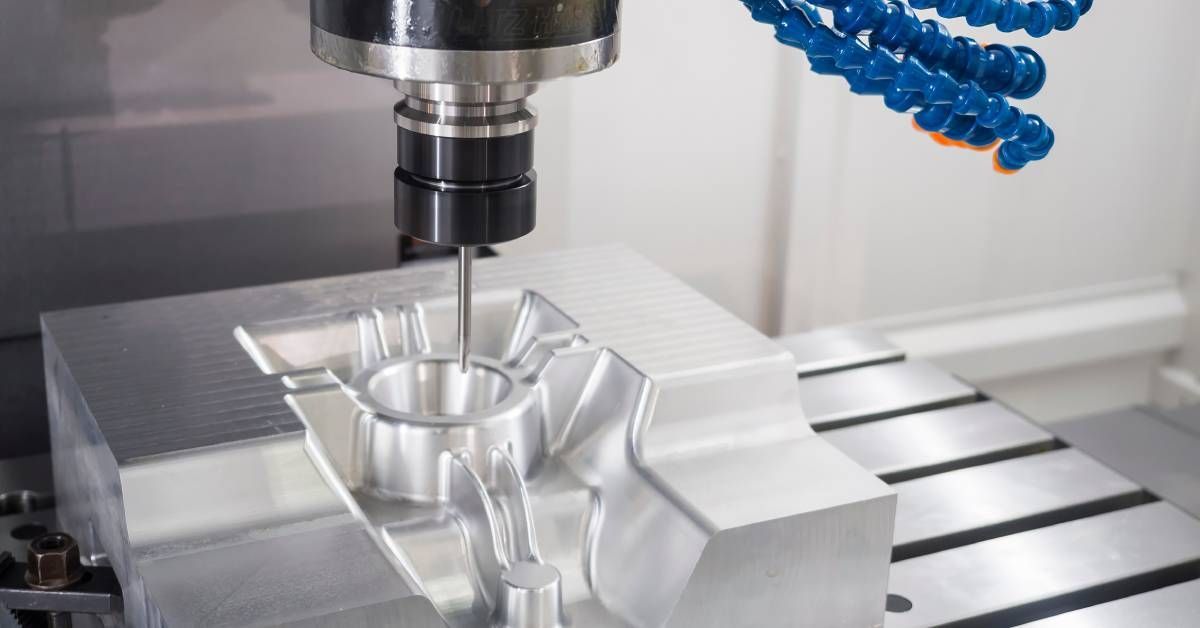
CNC Machining
CNC machining revolutionizes the production process by automating machine control through computer programming. This method offers unparalleled precision and repeatability, making it ideal for high-volume production runs. With CNC machining, complex and intricate designs can be executed with consistency and efficiency, reducing waste and minimizing human error. Once the CNC program is written, the machine can produce identical parts with minimal supervision, allowing for faster production times.
While the initial setup can be costly, the long-term benefits of increased productivity and lower per-unit costs make CNC machining a favorable choice for large-scale manufacturing. Furthermore, advancements in technology continue to enhance the capabilities of CNC machines, enabling even greater levels of detail and versatility in machining operations.
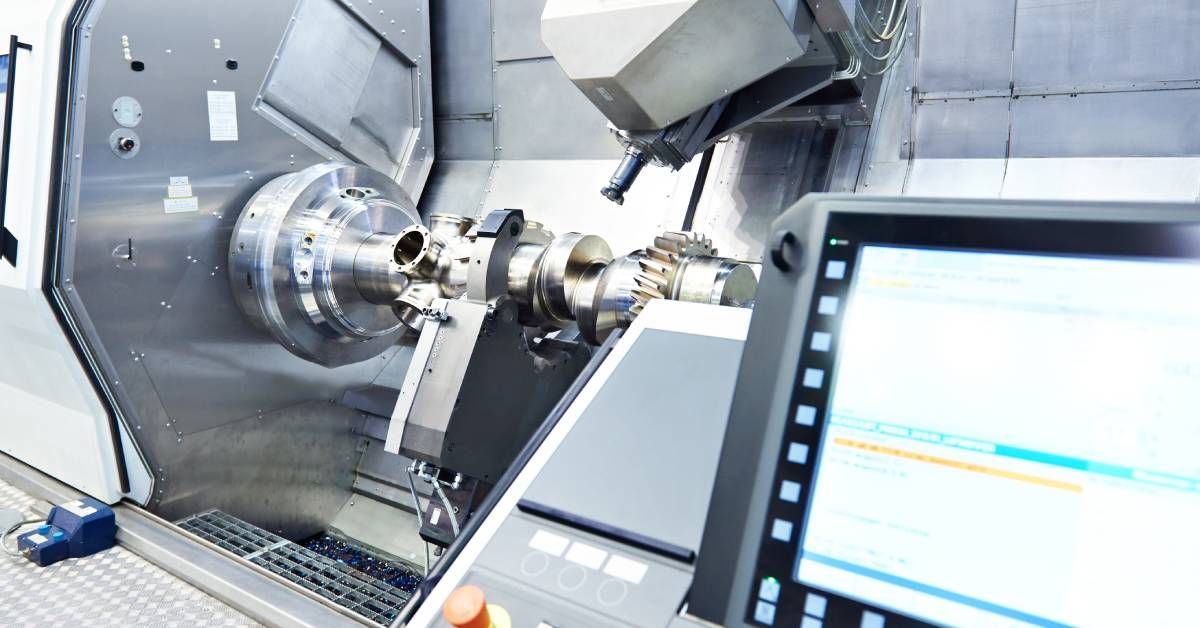

Key Differences
Comparing manual and CNC machining reveals several critical differences in key areas.
Flexibility and Adaptability
Manual machining offers greater flexibility and adaptability compared to CNC machining. Skilled machinists can make real-time adjustments to meet specific requirements or address unforeseen issues during the manufacturing process. This hands-on approach is well-suited for custom projects, low-volume production, and situations where precision and individual attention are essential. Conversely, CNC machining may not be as adaptable in the moment, but it excels in efficiency and precision through pre-programmed operations.
Production Efficiency
CNC machining significantly outpaces manual machining in production efficiency, especially for high-volume runs. Once programmed, CNC machines can produce consistent, high-quality parts with little need for additional human intervention, reducing production time and labor costs. Manual machining, by contrast, is generally more labor-intensive and time-consuming, making it less practical for large-scale manufacturing.
Cost Factors
The cost dynamics between the two methods vary. Manual machining is often more cost-effective for short production runs or one-off projects, given its lower setup expenses. However, the labor-intensive nature can increase costs for larger volumes. CNC machining involves higher upfront costs for programming and equipment setup but becomes more economical over long production runs due to its efficiency and reduced labor requirements.
Skill Requirements
Manual machining requires a high level of expertise and hands-on skills from the machinist, as they control the machining process directly. This provides valuable learning and skill development opportunities. On the other hand, CNC machining requires knowledge of computer programming and machine operation, emphasizing technical proficiency in programming and machine maintenance.
Suitability for Complex Designs
CNC machining excels in handling complex and intricate designs with high consistency and precision, which can be difficult to achieve manually. Its ability to execute detailed and repetitive tasks with minimal deviation makes it the preferred choice for intricate production needs. Manual machining may have trouble with such complex tasks, as it relies heavily on the machinist’s skill and precision.

Industries and Components That Rely on Each Process
There are many industries that use both manual and CNC machining.
Aerospace Industry
Manual machining is used to make custom prototypes, small batch parts for spacecraft, and repair components for aircraft. Meanwhile, CNC machining is used to make engine components, turbine blades, structural parts, and landing gear components.
Automotive Industry
Manual machining aids in making prototypes for custom vehicles and small batches of restoration parts. CNC machining helps make engine blocks, gearboxes, brake components, custom rims, and interior parts.
Medical Device Industry
Manual machining is used to make custom surgical tools and prototypes for medical instruments. CNC machining helps create prosthetics, implants, dental components, and precision instruments.
Electronics Industry
Manual machining is used for specialized enclosures and custom connectors. CNC Machining makes circuit boards, heat sinks, housings for electronic devices, and connectors.
Oil and Gas Industry
Manual machining is used in the repair and maintenance of parts and valve modifications. CNC machining is used for drill bits, valve components, piping components, and pump parts.
Defense and Military Industry
Manual machining helps in the creation of custom repair parts for field equipment and prototypes. CNC machining is used to make firearm parts, armor plating, vehicle and aircraft components, and precision optics mounts.
Each of these industries benefits from the unique advantages of manual and CNC machining, depending on their specific production needs and the complexity of the components required.
Future Trends in Machining
As technology continues to evolve, both manual and CNC machining are poised to face new trends and challenges that will shape their future. Understanding these trends is essential for manufacturers looking to stay competitive and innovative.
Integration of Smart Technology
The integration of smart technology and the Internet of Things is set to revolutionize the machining industry. In CNC machining, smart technology enables machines to communicate with each other, providing real-time data analytics and allowing for predictive maintenance and improved efficiency. Manual machining, while less directly affected, can benefit from IoT by optimizing workflows through enhanced monitoring of machine conditions and tool wear.
Advancements in Automation and Robotics
The rise of automation and robotics is prominently impacting CNC machining, enabling even greater productivity and precision. Automated systems can manage tool changes, part transfers, and quality inspections with minimal human intervention. While manual machining remains labor-intensive, there is potential for automation to assist in repetitive tasks, allowing machinists to focus on more complex aspects of their work.
Adoption of Additive Manufacturing Techniques
Additive manufacturing, or 3D printing, is being adopted alongside traditional machining methods to complement and enhance manufacturing capabilities. CNC machining is increasingly incorporating hybrid approaches, combining subtractive and additive techniques for efficient use of materials and innovative product designs. Manual machining may see a reduced role in such hybrid systems but can provide crucial finishing touches in prototype development.
Emphasis on Sustainability
Both manual and CNC machining are moving toward more sustainable practices. CNC machining can leverage precision and efficiency to minimize waste and reduce energy consumption. For manual machining, focusing on remanufacturing and repair work emphasizes resource conservation and extends product lifecycles.
Leverage the Full Potential of Machining
Manual and CNC machining represent two pillars of modern manufacturing, each serving unique roles based on specific needs. Manual machining provides adaptability and craftsmanship, while CNC machining excels in precision and efficiency. Understanding the differences between manual machining and CNC machining helps stakeholders make informed decisions about which approach aligns best with their goals.
Whether you are a seasoned professional or a newcomer to the field, the right approach can unlock new possibilities and elevate your manufacturing endeavors. At H&H Machine Services, we understand the importance of crating quality components. Let our prototype CNC machining services help you take your next project from idea to completion.