Tips for Optimizing Part Design for CNC Machining
CNC machining has revolutionized manufacturing processes for a variety of industries, from aerospace to electronics. Its combination of precision, speed, and versatility makes it invaluable for creating complex parts. However, poor design can lead to inefficiencies, higher costs, or even unusable parts. To truly harness the advantages of CNC machining, part design must be thoughtfully optimized.
This guide explores useful tips for optimizing part design for CNC machining. Whether you’re a designer, engineer, or manufacturer, these insights can help you streamline your workflow and achieve the best possible results.
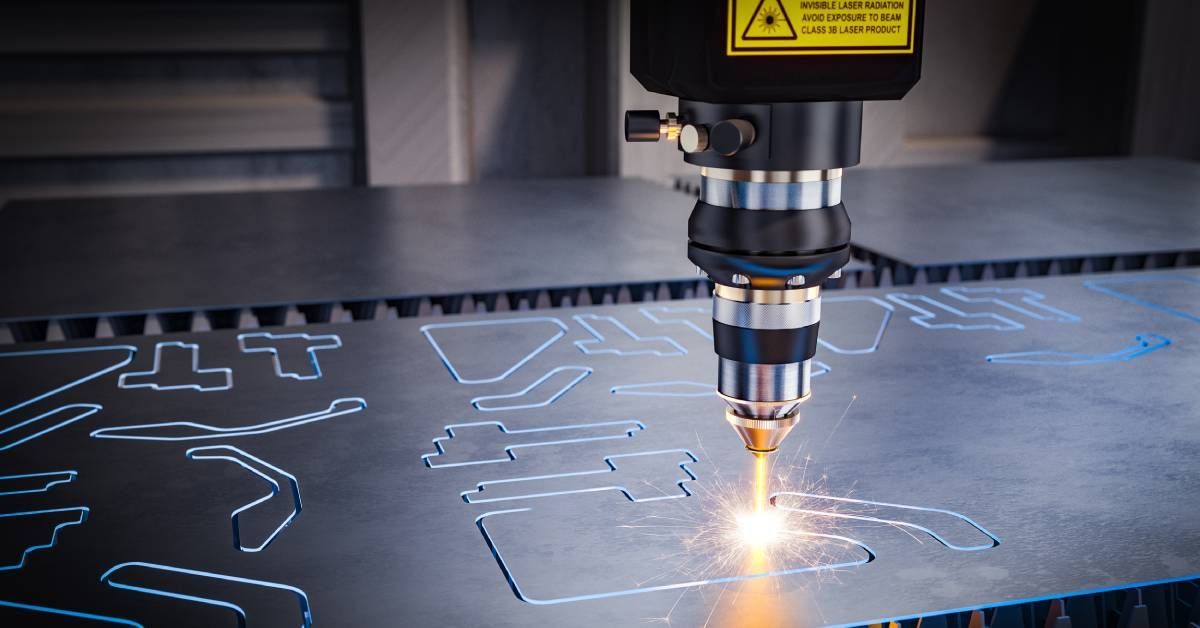

CNC Machining and Its Importance Across Industries
CNC machining uses pre-programmed computer software to operate precision machinery, such as lathes, mills, and routers. Unlike manual machining, CNC machining allows for automated, repeatable, and highly accurate part production, making it ideal for industries requiring exceptional precision.
From custom automotive components to medical implants, CNC machining supports a wide range of applications. However, its efficiency and accuracy are only as good as the designs it works with, underscoring the importance of optimizing part design.
The Basics of Part Design for CNC Machining
Before jumping into specific tips, it’s essential to understand the fundamentals of CNC machining, including:
- Material removal process: CNC machines remove material to create the desired shape. This subtractive process influences how features like slots, curves, and holes are made.
- Tool limitations: While CNC tools are highly precise, they’re limited in size, shape, and accessibility. This means features like undercuts may require special attention or additional steps.
- Machine compatibility: Designs must align with the capabilities of the CNC machine being used, whether it’s a 3-axis, 5-axis, or multi-axis machine. Complex designs often benefit from advanced machines but can also increase production costs.
- Tolerance and precision: While CNC machining achieves tight tolerances, specifying overly restrictive tolerances can increase costs unnecessarily.
Now that we’ve covered the basics, let’s explore some tips to ensure your part designs are CNC-friendly.
10 Tips for Optimizing Part Design for CNC Machining
Use Fillets To Replace Sharp Internal Corners
CNC tools are cylindrical, which makes sharp internal corners (90-degree angles) challenging to achieve. Instead, use fillets to match the cutting path of the tool. This reduces wear on tools and ensures better part accuracy.
Avoid Deep, Narrow Cavities
Deep cavities are challenging for tools to access and can cause vibrations that compromise precision. When possible, limit cavity depths to four times the diameter of the cutting tool. For deeper cavities, split the design into multiple sections for easier assembly.
Minimize Thin Walls
Thin walls can deform under cutting forces or during assembly, leading to inaccuracies. Design walls thicker than 0.8mm for metals and 1.5mm for plastics to ensure they remain stable throughout the machining process.
Choose Consistent Hole Sizes
Standard hole sizes (e.g., 3mm, 6mm, and 10mm) reduce the need for custom tools, improving efficiency and cost savings. Additionally, blind holes should be avoided if through-holes can achieve the same objective, as these are easier to machine.
Optimize Tolerances
Overly tight tolerances increase production time and cost. Instead of applying ±0.01mm tolerances everywhere, only include them on critical dimensions. Standard tolerances (±0.1mm) suffice for most non-critical features.
Consider Material Machinability
Material selection directly impacts machinability. Metals like aluminum and brass are more CNC-friendly compared to harder materials like titanium. Aluminum is lightweight, versatile, and affordable, making it ideal for prototypes, while brass offers excellent machinability and resistance to corrosion. Additionally, stainless steel provides durability but requires longer machining times. Discuss your material requirements with machinists to confirm compatibility with your design.
Limit Overhangs and Undercuts
Features such as overhangs and undercuts often require specialized tools or multi-axis machines, increasing complexity. Use minimal or no overhangs to streamline the machining process. Alternatively, you can split designs into multiple parts and assemble them later.
Leverage CAD and CAM Tools for Simulation
Modern CAD and CAM tools offer simulations to test designs before production. Run simulations to check for potential machining issues, such as inaccessible areas, tool collisions, and excessive material removal. Popular software options include Fusion 360, SolidWorks, and Mastercam.
Make Parts Easier To Secure
Parts that are difficult to clamp or secure during machining may result in errors. Add flat sections or holes that machining fixtures can grip easily. If the part requires machining on multiple sides, design symmetrical features to simplify reorientation.
Prototype and Iterate
Prototyping helps you identify design flaws early. Once your prototype is complete, evaluate its performance and gather feedback to refine the design. This iterative approach allows you to create better parts while improving the efficiency of future CNC runs.
Designs for Manufacturability
Designing for manufacturability ensures that parts are easy and cost-effective to produce. This includes keeping designs simple, with fewer intricate features and minimal excess material, standardizing dimensions for compatibility with off-the-shelf components, and collaborating with machinists to address potential production challenges. By keeping these basic principles in mind, you can optimize costs without compromising on performance.

Common Pitfalls in CNC Machining Design
Avoid these mistakes to keep your designs efficient and machinable:
- Overcomplicating designs: Avoid unnecessary complexity, such as intricate shapes or excessive surface finishes.
- Ignoring tool paths: Failing to account for the limitations of CNC tool paths can result in inaccessible features or compromised precision.
- Specifying too many tight tolerances: Excessive tolerances increase costs and machining time significantly.
Taking the time to make sure your CNC machining design process is up to date with industry best practices is the first step in achieving the results you want.
Future Trends in CNC Machining and Design Optimization
The future of CNC machining is set to be shaped by advancements such as:
- AI-assisted design: Predictive algorithms can optimize designs automatically for cost and manufacturability.
- Additive-subtractive hybrid machines: Combining CNC machining with 3D printing will lead to greater design flexibility.
- Real-time monitoring: IoT-enabled machines can adjust toolpaths dynamically based on live feedback.
Staying informed about these trends can give designers and manufacturers a competitive advantage.
Take Your CNC Designs to the Next Level
Getting the results you want from CNC machining requires a balance of creativity and practicality. Armed with these practical tips for optimizing part design for CNC machining, you can maximize efficiency, reduce costs, and achieve greater accuracy.
Is your equipment ready to handle the task at hand? At H&H Machine, we understand the importance of getting the results you want the first time. Our CNC machine repair service will ensure your equipment is ready to go when it’s time to scale production. Reach out today to see how we can help improve your manufacturing process and get you back on track!