What Is CNC Machining, and How Does It Work?
When manufacturers need precision and automation, CNC machining is often the first place they turn. This revolutionary technology has reshaped how parts are designed and made across industries. Whether for manufacturing the intricate components of an aircraft or the custom parts of a smartwatch, CNC machining is the backbone of modern production processes.
But what is CNC machining, and how does it work? We’ll delve into everything you need to know about this modern technology, exploring its history, features, and use cases, as well as the trends shaping its future.
A Brief History of CNC Machining
Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machining didn’t happen overnight. Its origins trace back to the 1940s and 1950s, a time when traditional punch card systems were adapted to control machinery. These early machines relied on preprogrammed instructions to execute precise actions, a leap forward from manual machining.
The real development began when CNC machines adopted software-based instructions. By the late 20th century, CNC technology advanced with computer-aided design (CAD) and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM), making it increasingly accurate, efficient, and user-friendly. Today, CNC machining is integral to countless industries, paving the way for rapid innovation and scalable manufacturing processes.

The Basic Principles of CNC Machining
At its core, CNC machining involves the use of computers to control machine tools. Here’s how it works.
Automation Through Programming CNC machining
operates by following coded instructions programmed into a computer. These instructions, often written in G-code, dictate the movement, speed, and tools used to shape a material into the desired form. This automation ensures precision and repeatability.
Multi-Axis Movement
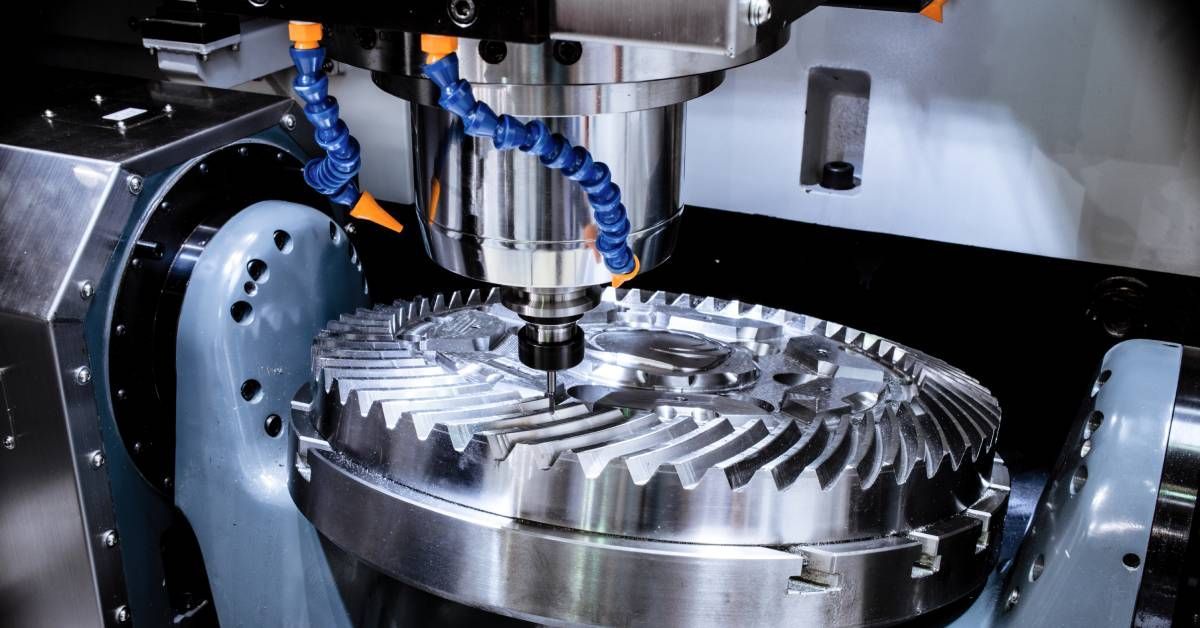
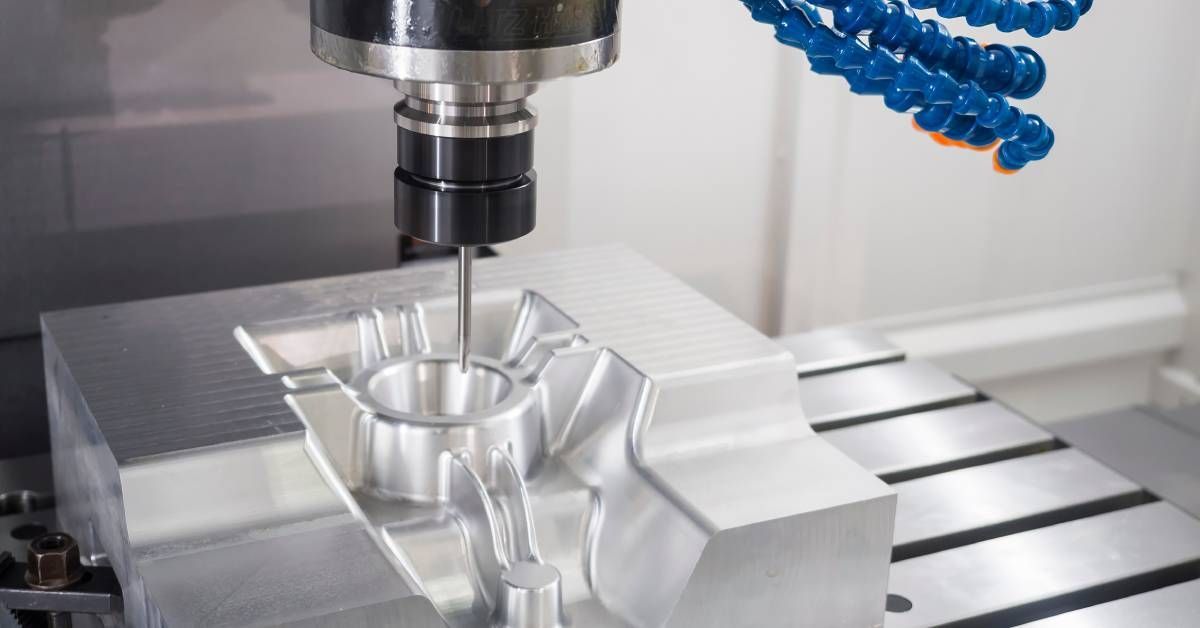
CNC machines are capable of operating along multiple axes, allowing for complex, intricate shapes to be produced. Basic machines operate on three axes (X, Y, Z), but advanced models can include additional rotations or movements, enhancing flexibility and complexity.
Material Removal Process
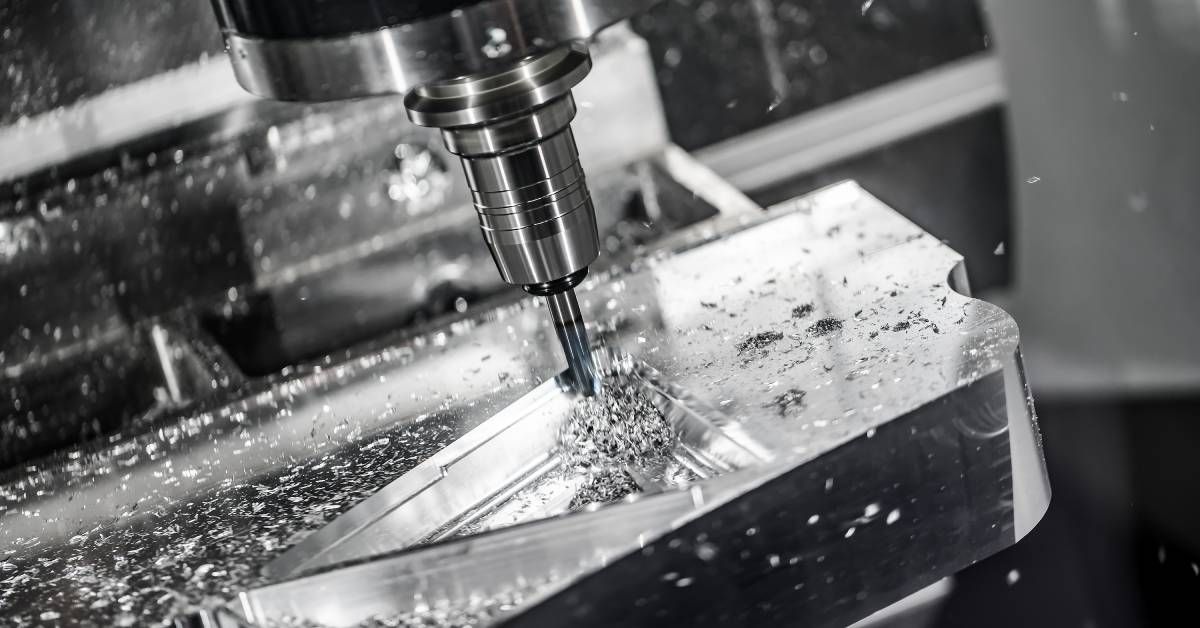
CNC machining is a subtractive manufacturing process, which means it removes material from a larger block, known as the workpiece, to create the final product. Tools such as drills, lathes, and mills are employed to cut, carve, or shape the material.
Precision and Tolerance
One of the distinguishing features of CNC machining is its exceptional accuracy. Tight tolerances can be maintained across production runs for uniformity. This attention to detail is essential for parts that require exact specifications in industries such as aerospace and health care.
Versatility in Materials
CNC machining can work with a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, wood, and composites. This versatility makes machining suitable for diverse applications, from automotive parts to custom prototypes.
Key Components of a CNC Machine
Every CNC machine, regardless of its type, includes several critical components:
- Controller: The controller is the computer that interprets G-code and executes commands.
- Machine bed: The sturdy foundation on which materials are placed is known as the machine bed.
- Cutting tools: These tools include drills, mills, and lathes designed for precise operations.
- Motors and drives: These power the movement of the machine’s axes (X, Y, and Z).
- Spindle: The spindle is responsible for rotating cutting tools or materials.
- Cooling system: The inclusion of a cooling system prevents overheating during high-speed machining.
Together, these components ensure that CNC machines operate smoothly and deliver consistent results.
Types of CNC Machines
CNC machinery comes in various forms, each designed for a specific function. Here is more information on the most common types.
CNC Milling Machines
These machines use a rotating multipoint cutting tool to remove material from a workpiece. Milling machines are perfect for creating complex designs and three-dimensional parts.
CNC Turning Machines
Also known as lathes, these machines rotate the workpiece against a stationary cutting tool for operations like threading, boring, and grooving.
Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM)
EDM uses electrical discharges to shape conductive materials. It’s often used for precision components that are difficult to machine with conventional tools.
Water Jet Cutters
Water jet cutters use high-pressure water and abrasives to precisely cut materials like stone, metal, and glass.
Plasma Cutters
Plasma cutters use high-energy gas to melt and remove material, making them ideal for cutting thick metal plates. These machines form the backbone of modern manufacturing, enabling businesses to produce precise, high-quality components.
Industries That Rely on CNC Machining
CNC machining is so versatile that it finds applications across a wide range of industries:
- Aerospace: Creating high-precision components like engine parts and airframes is easier with CNC machining.
- Automotive: Manufacturing complex parts for engines, transmissions, and interiors in the automotive industry is led by CNC machine technology.
- Medical devices: CNC machining is valuable for producing implants, surgical instruments, and diagnostic devices.
- Electronics: The electronics industry counts on machining for crafting intricate parts for circuit boards and mobile devices.
- Defense: Fabricating critical tools and equipment with absolute accuracy is reliant on CNC machining.
- Consumer goods: Lastly, making custom parts for products like sports equipment, kitchen appliances, and toys today comes down to this form of machining.
From prototyping new designs to full-scale manufacturing, CNC machining is indispensable to industries where quality and precision are nonnegotiable.

Advantages of CNC Machining
Why has CNC machining become the go-to solution for manufacturers worldwide? Here are some of its most notable benefits:
- Unparalleled precision: CNC machining achieves intricate cuts and designs with minimal error.
- High speed and efficiency: Using this form of machining reduces production time compared to manual options.
- Consistency: You can count on consistency and accuracy, even during high-volume production runs.
- Versatility: CNC machines handle a range of materials, including metal, plastic, wood, and more.
- Cost-effectiveness: Using this form of machining reduces material waste and minimizes human labor.
- Automation: Since CNC machines operate autonomously, they require minimal human intervention.
These advantages make CNC machining ideal for small-scale prototyping and large-scale manufacturing alike.
The Future of CNC Machining: Trends and Innovations
The future of CNC machining is bright, driven by technological advancements and evolving industry needs. Here are some trends to watch:
- AI-powered automation: CNC machines are increasingly integrating artificial intelligence, enabling smarter operations and predictive maintenance.
- Five-axis machining: Advanced CNC machines now support five-axis movement to produce even more intricate geometries.
- Sustainability: Newer technologies focus on reducing material waste and optimizing energy consumption.
- Hybrid machining: Combining CNC machining with 3D printing technology to create hybrid approaches for complex projects is the new trend.
- Cloud integration: Remote monitoring and programming of CNC machines via the cloud enhance flexibility and efficiency.
These innovations are set to make CNC machining even more accessible, adaptable, and sustainable.
When To Outsource CNC Machining Needs
Outsourcing CNC machining can be a strategic decision for businesses looking to optimize resources and streamline production. It’s often ideal to outsource when in-house capabilities are insufficient to meet complex design specifications or production volumes. Additionally, if your company lacks the necessary machinery or expertise to handle specialized materials and intricate geometries, outsourcing to a trusted CNC machining provider ensures precision and quality.
Outsourcing is also beneficial for managing costs when scaling up production, avoiding major investments in equipment, or reducing lead times for urgent projects. By partnering with experienced CNC service providers, businesses can focus on their core operations while maintaining high standards for manufactured components.
Precision Meets Possibility
CNC machining is a game changer for industries striving to achieve precision, efficiency, and scalability. From jet engines to prosthetic limbs, this machining powers the innovations that define our modern world. Understanding what CNC machining is and how it works enables manufacturers to leverage this modern technology for improved productivity and project management.
Are you ready to see what CNC can do for you? At H&H Machine Service, we offer reliable and professional expertise, allowing you to get the most out of your next project. Our CNC machining services have everything you need to support your manufacturing goals!